
An artist's depiction of CSIRO's Parkes radio telescope receiving the polarised signal from the new 'fast radio burst'. (Image: csiro.au)
作者:顾为民、董一泽、刘彤、马任意、王俊峰
快速射电暴(FRB)是近年来用大型射电望远镜探测到的毫秒时标的射电脉冲现象,其对应的物理机制尚不清晰。从2007年至今,天文学家利用澳大利亚的Parkes、美国的Arecibo和GBT这三个射电望远镜共探测到了17个FRB。在这17FRB中,121102这个源由于近期观测到它存在重复爆发行为而格外引人注目。截止2015年底该源共已探测到17个重复暴。天文系的研究团队提出了 一个由强偶极磁场中子星与强磁场白矮星所组成的半相接双星模型,其间歇性的洛希瓣外流机制可以较好解释快速射电暴的辐射频率和持续时间,并且该模型结果与连续观测中两个相邻爆发的间隔时间相符合。该论文于5月8日被天文学权威期刊《ApJ Letters》接受发表。特别指出,天文系第一届本科生董一泽同学对该项工作有重要贡献,是论文的第二作者。
论文预印本链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/1604.05336
英文摘要:
We propose a compact binary model for the fast radio burst (FRB) repeaters, where the system consists of a magnetic white dwarf (WD) and a neutron star (NS) with strong bipolar magnetic fields. When the WD fills its Roche lobe, mass transfer will occur from the WD to the NS through the inner Lagrange point. The accreted magnetized materials may trigger magnetic reconnection when they approach the NS surface, and therefore the electrons can be accelerated to an ultra-relativistic speed. In this scenario, the curvature radiation of the electrons moving along the NS magnetic field lines can account for the characteristic frequency and the timescale of an FRB. Owing to the conservation of angular momentum, the WD may be kicked away after a burst, and the next burst may appear when the system becomes semi-detached again through the gravitational radiation. By comparing our analyses with the observations, we show that such an intermittent Roche lobe overflow mechanism can be responsible for the observed repeating behavior of FRB 121102.
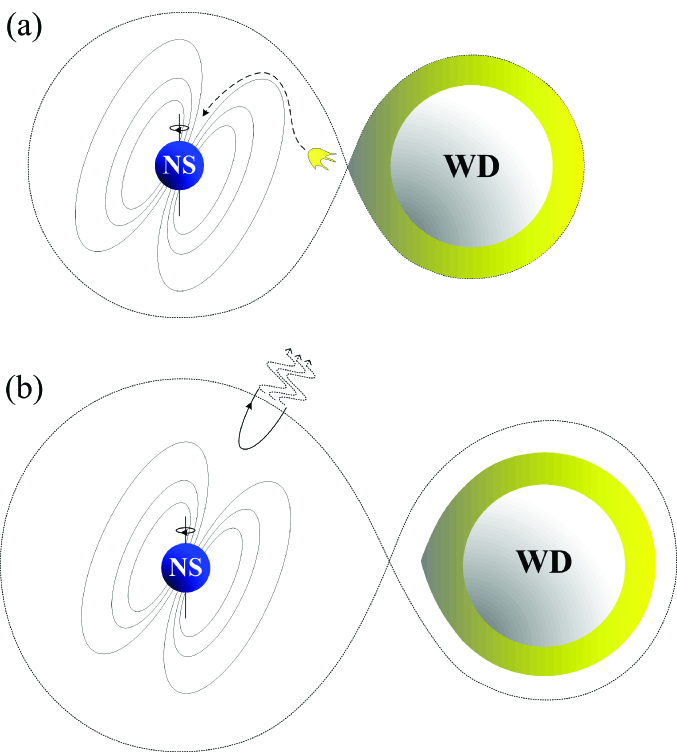
图:(a)白矮星的大气物质通过内拉格朗日点被中子星吸积;(b)被吸积的物质在中子星表面附近发生磁重联,触发快速射电暴。同时,由于角动量守恒,白矮星被弹开。随后,由于引力波辐射两个致密天体将不断靠近。当白矮星再次充满洛希瓣时,有可能再一次触发快速射电暴。