This study aims to explain the anomalous deep absorption in one of the most massive supermassive black hole from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR 7 catalog. According to Shen et al. 2011, it has MBH = 1011.205 solar masses. Our continuum-fit approach suggests a substantially smaller BH mass, which is 3.52×109 solar masses.
SDSS J110511.15+530806.5 exhibits exceptional deep absorptions in the optical/UV domain. The disk, hot corona and warm emission is affected by absorbing gas. Using XSPEC models we were able to model such deep absorption with two Gaussians. The deep absorption shows evident velocity shifts. The velocities of the detected absorbers lie in the range 6330-108135 km/s. The corresponding mass outflowing rate is as large as 38.5% of the accretion rate.
The high absorption observed in SDSS J110511.15+530806.5 is evidence of fast winds that place the source in the group of objects on the border with UFO (ultra-fast outflows), strong broad absorption line, and fast failed radiatively accelerated dusty outflow (FRADO). This absorption affects the BH mass measurement by two orders of magnitude as compared to the virial mass estimation.
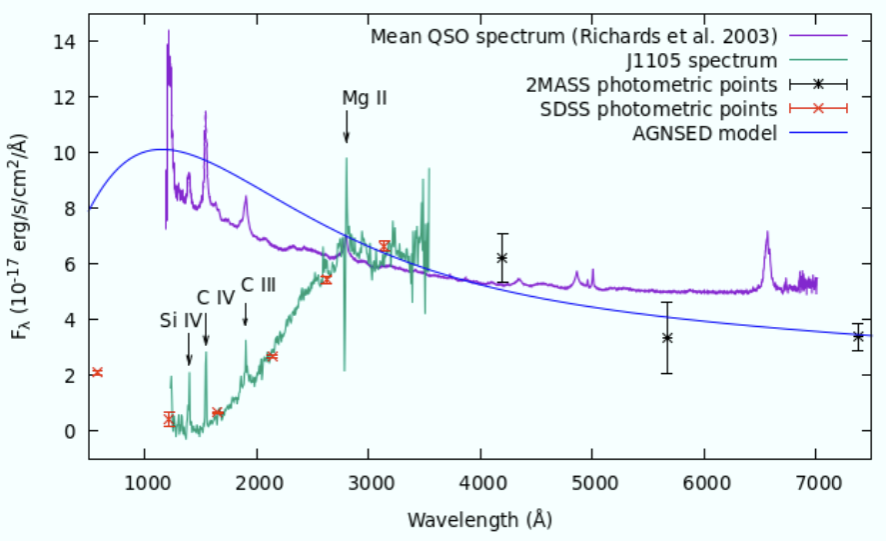
Figure 1. The J1105 spectrum in the SDSS Data Release 14 (green line) in comparison with the mean QSO spectrum (purple line) by Richards et al. (2003).
This paper has been published in A&A and can be accessed from: https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2022/12/aa44417-22/aa44417-22.html This work was led by Dr. Marcin Marculewicz, a postdoc of the Department of Astronomy, Xiamen University. The co-authors are: Prof. Marek Nikolajuk (University of Białystok) and Prof. Agata Różańska (Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center).